As someone considering retiring in Thailand during the later stages of life, the recent changes in Thai tax regulations have prompted a reevaluation of the financial landscape for expatriates and retirees like myself. These new rules, set to take effect from January 1, 2024, bring about a significant shift in taxing foreign-earned income for Thai tax residents, potentially altering the appeal of holding a retirement visa.
Understanding the New Regulations
Thailand, a country known for its rich culture, stunning landscapes, and vibrant lifestyle, has recently introduced new tax regulations that may significantly impact Thai tax residents earning income from abroad. Effective from January 1, 2024, these regulations mandate personal income tax obligations for residents bringing foreign-earned income into Thailand within a calendar year.
Previously, Thai tax residents were not required to pay personal income tax on foreign-earned income if it remained outside the country. However, the implementation of these new rules alters the landscape. Residents who bring in income generated abroad will now be subject to personal income tax in Thailand.
This shift places a greater onus on tax service providers and individuals to maintain meticulous records and engage in comprehensive administration around financial data. Failure to comply with these regulations could lead to penalties or legal consequences, necessitating a heightened level of vigilance and compliance among affected taxpayers.
Impact on Retirement Visa Holders
Initially drawn to the idea of a retirement visa in Thailand due to its attractive lifestyle and relaxed atmosphere, I now find myself pondering the implications of these tax amendments. Previously, retirees like me could enjoy residing in Thailand while earning foreign income, often exempt from Thai taxation. However, with the revised regulations, this exemption may no longer apply if I bring my overseas earnings into the country.
This change forces a reconsideration of my financial plans and obligations as a prospective retiree in Thailand. The increased record-keeping and administrative responsibilities, coupled with potential tax liabilities on foreign-earned income, require a more thorough assessment of the practicality of obtaining a retirement visa under the new tax regime.
Comparative Analysis of Individual Taxation in Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, and Taiwan
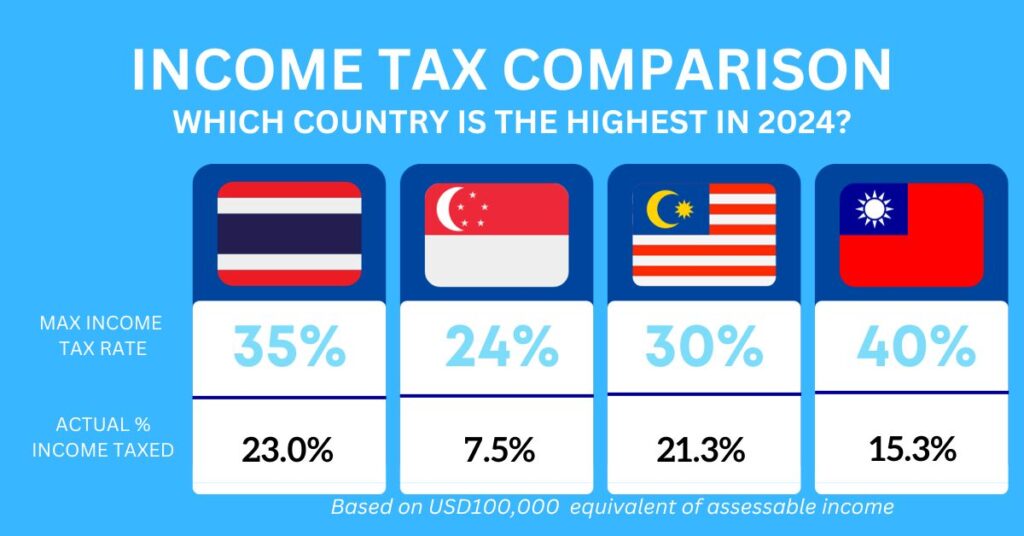
Understanding the tax frameworks in neighboring countries offers valuable insights for individuals seeking comparative analysis and potential options. Here’s a brief overview of individual taxation from 2024 onwards in Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, and Taiwan:
Thailand:
- Progressive tax rates range from 0% to 35%.
- Deductions and exemptions for various expenses and allowances.
- Tax residency status determined by days spent in Thailand. A person that stays in Thailand for 180 days or more in a tax year shall be considered a tax resident of Thailand for that year, under the Revenue Code.
Singapore:
- Progressive tax rates from 0% to 24%.
- Taxed based on residency status (resident or non-resident).
- Comprehensive list of tax reliefs and rebates available.
- Tax exemption on foreign-sourced income for residents not brought into Singapore.
Malaysia:
- Progressive tax rates range from 0% to 30%.
- Resident status based on days present in Malaysia.
- Tax incentives for certain investment activities.
- Partial tax exemption on foreign-sourced income for residents.
Taiwan:
- Progressive tax rates from 5% to 40%.
- Tax residency determined by days spent in Taiwan.
- Various deductions and exemptions available.
- Tax exemption or reduction for certain foreign-sourced income for residents.
Existing retirement visa holders must consult with their own tax professionals to understand the implications of these changes on their financial planning and compliance requirements.
Important Reminders For Retirement Visa Holders
90-day Reporting
Retirement visa holders are required to notify the Immigration Office regarding their current residential address every 90 days. This can be done either by mail, by personal visit to the immigration office, or online. You may also enlist the services of our company to do this on your behalf with a Power of Attorney.
Re-entry Permit
If you plan to travel in and out of Thailand during the year of your visa validity, you will need a multiple re-entry permit. This will insure that your visa does not get cancelled. In case you find the need to leave the country for whatever reason, you can apply for a re-entry permit at the international airport before leaving the country. Or you can simply contact us and we can get you a re-entry permit in 1 day.
Considering Employment Visa Alternatives
Consequently, the prospect of holding an employment visa instead of a retirement visa now merits exploration. While employment visas come with their own set of requirements and responsibilities, the tax implications may differ. With an employment visa, income earned within Thailand and from overseas might be subject to taxation, but the intricacies might vary, warranting a closer examination of the overall tax burden.
Comparatively, other countries in the region, such as Singapore, Malaysia, and Taiwan, offer different tax frameworks for residents and expatriates, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Assessing the individual taxation systems of these countries becomes crucial in making an informed decision about retirement or employment abroad.
Conclusion: Navigating the Changing Landscape
The decision to retire or “work” in Thailand, especially considering the evolving tax regulations, demands a meticulous understanding of the financial implications. While the allure of Thailand’s lifestyle remains strong, the impact of the new tax rules on retirement visa holders necessitates careful consideration.
As I deliberate on my retirement options, it’s apparent that seeking professional advice from my tax experts and advisors specialized in international taxation will be essential. This guidance will provide insights into the most prudent visa options, whether it’s pursuing a retirement visa, an employment visa, or exploring alternatives in neighboring countries.
The evolving tax landscape in Thailand underscores the importance of staying informed and agile in adapting to regulatory changes. Ultimately, making a well-informed decision about retirement or employment in Thailand involves weighing the lifestyle benefits against the tax implications, ensuring a harmonious balance between financial security and the desired quality of life.
